Damp Proofing

Damp proofing refers to a range of techniques and materials used in construction to prevent the penetration of moisture into buildings from the ground or external sources. Its primary purpose is to protect the structural integrity of buildings and maintain a healthy indoor environment by controlling dampness, which can cause damage, decay, and mould growth.
Types of Dampness Addressed
- Rising Damp: Moisture from the ground that travels upwards through porous building materials such as bricks or mortar by capillary action.
- Penetrating Damp: Water that enters the building through defects in walls, roofs, or windows due to rain or leaks.
- Condensation Damp: Moisture that forms on cold surfaces inside buildings due to high humidity and inadequate ventilation.
Common Damp Proofing Methods
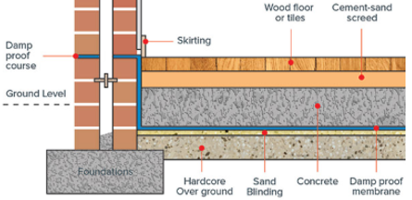
- Damp Proof Course (DPC): A physical barrier, usually a layer of plastic, bitumen, or slate, installed in the walls near the ground level to prevent rising damp. It interrupts the capillary action of moisture moving upwards.
- Damp Proof Membrane (DPM): A continuous sheet of impermeable material, typically polyethylene, laid beneath concrete floors or in walls to prevent moisture ingress from the ground.
- Waterproof Coatings and Sealants: Applied to external walls or foundations to repel water and prevent penetrating damp.
- Chemical Damp Proofing: Involves injecting chemical solutions into walls to create a water-repellent barrier that stops rising damp.
- Ventilation and Insulation: Measures to reduce condensation damp by improving air circulation and maintaining surface temperatures.
Importance of Damp Proofing
- Structural Protection: Prevents decay and weakening of building materials such as timber and masonry.
- Health and Comfort: Reduces mould growth and damp-related health issues like respiratory problems.
- Energy Efficiency: Dry buildings retain heat better, reducing heating costs.
- Property Value: Proper damp proofing maintains the value and longevity of a property.
Damp proofing is a fundamental aspect of building construction and maintenance, aimed at controlling moisture ingress and its damaging effects. By employing appropriate damp proof courses, membranes, coatings, and ventilation strategies, buildings can be safeguarded against damp-related problems, ensuring durability, safety, and comfort for occupants.