X-Ray Protection
X-ray protection is a critical aspect of safety in medical, dental, industrial, and research environments where ionising radiation is used. The primary goal is to shield personnel, patients, and the public from unnecessary exposure to X-rays, which can be harmful to living tissues. X-ray protection involves the use of specialised materials such as lead-lined boards, radiation shielding boards, and fillers to create barriers that absorb or block harmful X-rays. Lead-lined boards remain the gold standard due to their effectiveness and ease of use, while fillers and composite boards offer flexible alternatives for various applications. Ensuring compliance with safety standards is paramount in protecting health and safety in environments where X-rays are utilised.
Key Components of X-Ray Protection
1. Lead-Lined Boards
Lead-lined boards are one of the most common and effective materials used for X-ray shielding. These boards consist of a core material, often plasterboard or fibreboard, which is lined or impregnated with a layer of lead. Lead is highly effective at absorbing X-rays due to its high density and atomic number, significantly reducing radiation transmission.
- Applications: Lead-lined boards are widely used in the construction of X-ray rooms, walls, doors, and ceilings in hospitals, dental clinics, and laboratories.
- Advantages: They provide robust protection, are relatively easy to install, and can be cut and shaped to fit specific architectural requirements.
- Thickness: The thickness of the lead lining varies depending on the level of protection required, typically ranging from 0.5mm to 2mm of lead equivalence.
2. X-Ray Protection Boards
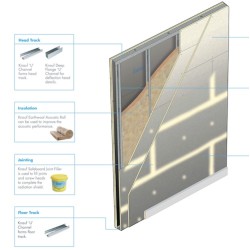
These are specialised boards designed specifically for radiation shielding. They may incorporate lead or other heavy metals and are engineered to meet regulatory standards for radiation protection.
- Types: Common types include lead-lined plasterboards, lead composite boards, and lead-free alternatives that use materials such as barium or tungsten.
- Installation: These boards are used in walls, partitions, and ceilings to create barriers that prevent X-ray penetration.
- Benefits: They offer a balance between structural integrity and radiation protection, often providing fire resistance and soundproofing alongside shielding.
3. Fillers for X-Ray Protection
Fillers are materials used to enhance the radiation shielding properties of construction elements. They are often mixed into plaster, concrete, or other building materials to increase their density and X-ray attenuation capabilities.
- Common Fillers: Lead powder, barium sulphate, and tungsten compounds are frequently used as fillers.
- Usage: Fillers are incorporated into wall panels, floor screeds, and ceiling tiles to provide additional protection without the need for thick lead sheets.
- Advantages: They allow for more versatile construction options and can reduce the overall weight and cost of shielding structures.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
X-ray protection materials and installations must comply with national and international safety standards, such as those set by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the UK and the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Proper design, installation, and maintenance of shielding are essential to ensure effective protection.